
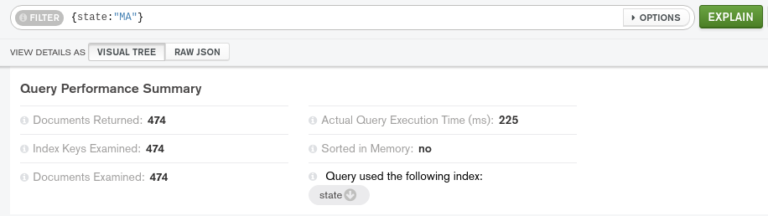
An example of this is shown in the figure: (a) averaging happens across documents within a group (b) averaging happens over values within a document. However, some accumulators can be used in other stages but not as accumulators, that is, they don't maintain state. These can be used only in some stages: $bucket, $bucketAuto, $group and $setWindowFields. They maintain their state as documents pass through the pipeline.

Developers can write custom JavaScript functions (MongoDB 4.4) for these.Īccumulators are special expression operators that compute totals, maxima, minima and other values. Custom expression operators include $accumulator and $function. There are many categories of expression operators: arithmetic, Boolean, comparison, conditional, data size, date, literal, object, set, string, text, trigonometry, type, etc.
#Mongodb compass count code#
By becoming familiar with these, developers can simplify their application code by doing most of the processing in MongoDB. Source: Adapted from MongoDB Docs 2021h.Īn expression operator has a name and takes either an array of arguments or a single argument. What are expression operators in MongoDB aggregation?Īveraging as accumulator and non-accumulator.$unwind: Given an array field, outputs one document per array element.$sort: Reorders document stream by a specified sort key.Operator $unset is an alias for removing fields. $project: Reshapes documents by adding or removing fields.$merge: Writes the output to a collection.$match: Filters documents based on standard MongoDB queries.$lookup: Does a left outer join to another collection in the same database.$limit: Passes only the first n documents to the next stage.If specified, applies an accumulator expression for each group. $group: Takes an identifier expression for grouping input documents.$count: Count number of documents at this stage.$addFields: Add new fields to documents.Except for $out, $merge and $geoNear, other stages can appear multiple times in a pipeline. Could you describe some aggregation pipeline operators or stages?Īn aggregation pipeline is constructed with the aggregate() method of the Collection class and takes an array of stages: db.collection.aggregate( ).While handy, these lack the flexibility and capability of the aggregation pipeline. Single Purpose Aggregation Methods: From the Collection class, the methods estimatedDocumentCount(), count() and distinct() aggregate from a single collection.Aggregation pipeline is now the preferred approach since it offers better performance and usability. Map-Reduce Function: This legacy approach was deprecated in MongoDB 5.0.Some stages can use indexes for better performance. The aggregation pipeline can operate on a sharded collection.

Other stages do sorting, grouping, string concatenation, array processing, and so on. Among the basic stages are filters that obtain a subset of matching documents and transforms that reshape data into a suitable output form. Each stage does specific processing on the data. Aggregation Pipeline: We can think of data as moving along a multi-stage pipeline.There are three ways to do aggregation in MongoDB: What are the ways to do aggregation in MongoDB?.While being flexible and intuitive for developers, MongoDB's aggregation is not as performant as some other databases or tools. These are good reasons for using MongoDB's aggregations. Sometimes we don't want to copy data and process it elsewhere. We wish to perform some computations on the data or report on live data. Often just retrieving data is inadequate. Therefore it's really a Turing complete functional language. MongoDB's aggregation framework can do any kind of processing. Aggregation framework or pipeline is the manner in which MongoDB does data processing in the database layer. Source: Develop Paper 2019.ĭata can be processed in the application layer or in the database layer. An example aggregation pipeline of two stages.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
